Vehicleless Dispatching Vehicle Dispatching System Based on GPS/Beidou Satellite Technology
The modern vehicle dispatching system is a high-tech project integrating global satellite positioning technology (GPS), geographic information technology (GIS) and modern communication technology. It transmits information such as the dynamic position (longitude and latitude), time and state of the moving target to the control center through the wireless communication link in real time, and then displays the moving target motion track on the electronic map with the geographic information query function. Monitor and query parameters of interest such as the position, speed, direction of motion and vehicle status of the target. At present, such systems mainly use the GPS/GSM method to complete the positioning communication requirements. However, the simple GPS/GSM vehicle scheduling system cannot fully meet the needs of daily life, such as in the remote western regions, deep mountains and old forests, etc. A very sharp problem is that without the GSM signal, or if the GSM signal is covered, the vehicle scheduling system is completely ineffective. In addition, due to strategic considerations, in some extraordinary periods (such as war), the United States may turn off GPS satellite positioning signals. If our system is completely dependent on GPS, it will inevitably cause great losses. Due to the above problems, we designed and developed a GPS/Beidou satellite-based system design to better solve these problems.
2 Introduction to the “Beidou†System At the end of 2000, China established the satellite positioning and navigation system of “Beidou No.1â€, a satellite navigation and navigation system independently developed by China. The system is a regional navigation system that provides satellite navigation information throughout the day and all day. It will mainly provide positioning and navigation services for transportation, transportation and offshore operations in China.
The same positioning system, China's "Beidou" positioning system and the United States' Global Positioning System (GPS) are different, GPS is passive (broadcast), can receive signals when received, the number of users is not limited, but can not achieve communication Function; while the "Beidou" positioning system is active (responsive), it establishes contact with the central station to achieve positioning function, and has communication function. The "Beidou" positioning system has the ability to combine communication and navigation. Two-way information exchange can be carried out by using two synchronous real-point satellites. The Beidou navigation and positioning satellite system supports 200 positioning or short-message services per second on the uplink and downlink respectively, which is much higher than the concurrent processing capability of Inmarsat-C/OmniTrack and other systems. The scope covers all areas and sea areas in mainland China, and is truly blind-free coverage compared to telecommunications cellular networks. The main components of the Beidou satellite navigation and positioning system are:
(A) Beidou Satellite: consisting of two geosynchronous satellites (one in-orbit spare satellite);
(B) Beidou Ground Control Center: consists of five parts: signal transmission and reception, information processing, scheduling, clock, test subsystem and supporting equipment;
(C) User machine: The terminal of satellite navigation and positioning user, the service scope is divided into two types: ordinary type and command type. Each command-type user machine can control 100 ordinary user machines; ordinary user machines are divided into four types according to the carrying mode: portable, vehicle-mounted, ship-borne, and airborne.
3 System overall architecture The system consists of vehicle terminal, communication link, central server and monitoring terminal. The overall structure is shown in Figure 1. The vehicle terminal completes the positioning of the vehicle, the storage of the trajectory and the information transmission, the wireless communication link completes the information interaction, the central server completes the connection with the vehicle terminal and the monitoring terminal and the data storage, and the monitoring terminal completes the monitoring of the vehicle.
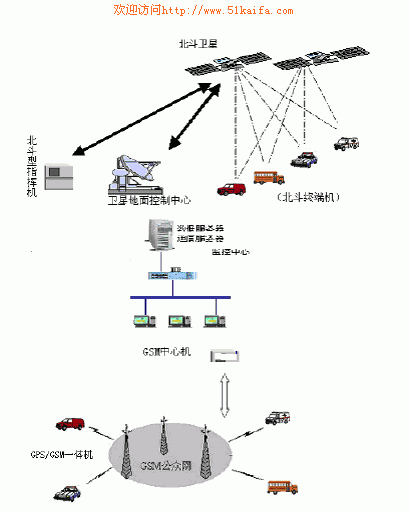
Figure 1 Overall structure of the system
3.1 System working principle
When the scheduling information appears, the vehicle GPS receiver accepts the positioning data of the GPS satellite, calculates its own geographical location latitude and longitude coordinates, and then sends the position, status, and alarm information to the control center through the GSM module of the vehicle station, and stores it in the database; When the GSM signal cannot be captured, the Beidou satellite positioning system is enabled. The system has the dual functions of positioning and communication, and transmits the position and status of the vehicle to the control center through the satellite system.
3.2 Introduction of the vehicle unit The vehicle unit is divided into a GPS part and a “Beidou†part.
GPS vehicle equipment uses GSM/GPS integrated machine, equipped with standard serial port, which can output NEMA-0183 standard GPS positioning data. In addition, the vehicle equipment can carry out voice call and data communication. Under normal circumstances, the vehicle station passes GSM SMS mode and control center. contact.
The "Beidou" part selects the vehicle-mounted user terminal, and its technical indicators are:
Beam width: pitch direction: 25° to 90°; horizontal direction 0° to 360°;
Frequency: Adopting L/S band transmission/reception, strong anti-rain aging ability, attenuation of rain fog is less than 0.3dB;
Number of receiving channels: ≥ 2;
First capture time: ≤ 4 seconds;
Lost lock recapture time: ≤ 1 second;
Receive signal error rate: ≤10-5;
Transmit EIRP value: ≥13 dBW;
Transmit frequency offset: ≤ 2 × 10-7;
Transmit signal power stability:
±0.5dB (the longest transmission signal period);
±1 Db (24 hours, working environment conditions);
Transmit signal carrier suppression: ≥30 dB;
Power consumption: DC 10 ~ 32V ripple ≤ 1%, with power logic control function;
Standby sleep state power consumption: 300mW;
Average power consumption: ≤6W;
Maximum transmission power: ≤20W;
When the GSM signal can be received, the information of the onboard unit (location and other request service information) transmits GPS positioning information and sends a message through the GSM network; when the GSM signal is not received, the positioning communication function of the "Beidou" system is used to install The Beidou user machine on the moving target sends a positioning request to the positioning station through the satellite. The positioning station calculates the longitude and latitude of the target position according to the received two satellite signals, and transmits it back to the user machine through the satellite, and the user machine obtains The location information, at the same time, the commander to which the user machine belongs also obtains the location information. The commander transmits the location information directly to the positioning data server and GIS server connected thereto, and displays the location of the vehicle on the electronic map. The monitoring center personnel implement effective scheduling and monitoring of the vehicle according to the intuitive graphic information, and complete the data communication from the moving vehicle to the user command and control center through the above process.
3.3 Introduction of Control Center This system adopts the working mode of joint control of C/S structure combined with main control center and acceptance station. The main control center is composed of a database subsystem, a communication subsystem and a call acceptance subsystem; the receiving station includes a communication subsystem, a main control center of the GIS subsystem, and each receiving station form a computer network through dedicated lines, exchange data and share information with each other to realize the group. Dispatching, networked alarms, and high security requirements.
The structure of the control center is shown in Figure 2.
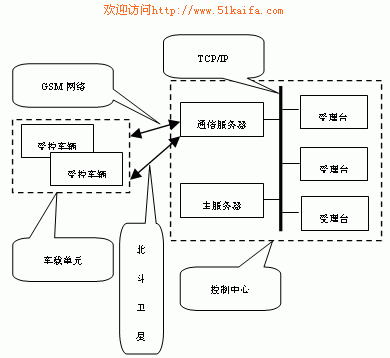
Figure 2 Control Center Block Diagram
3.4 Main functions of the system Vehicle tracking monitoring:
Tracking and monitoring the position of the moving vehicle (including longitude and latitude), and visually displaying the vehicle running position on the electronic map of the monitoring area. The positioning interval can be set autonomously.
Command and Control:
The monitoring center can perform voice or digital command dispatching on the vehicle through the call handle of the vehicle equipment.
Alarm acceptance:
When the vehicle alarms, the monitoring center will receive a prompt of the sound and light alarm, and at the same time, the screen of the alarm vehicle will be automatically tracked, and the distance indicator centered on the alarm vehicle will be displayed. According to the vehicle archive, various parameters of the alarm vehicle, such as the number, are displayed. , models, license plates, colors, owners and so on.
Vehicle control:
Taking relevant technical measures, after the vehicle is stolen, the monitoring center can make the vehicle unable to drive by means of remote control to make the vehicle power off, and also allow the vehicle to make a sound and light distress signal.
Vehicle management:
Combined with vehicle location information and status information, the vehicle and driver's working conditions can be effectively recorded and counted.
Data report output:
Daily and monthly alarm form record output, alarm location map, user usage report, login logout form output. The monitoring center can check the daily login or logout information of the vehicle, check the vehicle file, and print out the daily monitoring report.
Vehicle track playback:
The monitoring center can replay the past driving route of the controlled vehicle at any time.
Network management:
Network management of the main control center and the receiving station.
Information deployment:
The control center has the data of all users, and the geographic information and auxiliary information of all service areas, which can schedule the resources of the whole network system, and allocate the number of users who simultaneously realize various tracking among the user monitoring centers.
4 system software design The main modules of the software system are target location scheduling, data transmission, track playback, basic information management of mobile targets. The system adopts C/S structure, and realizes the fusion of “Beidou†system and GPS by using Windows Sockets, large database, TCP/IP network and MapX technology, and expands the application range. Its software flow chart is shown in Figure 3.
In the system software design, we use some mainstream technologies, making our system an open system, and fully consider the compatibility and scalability. In the implementation of data transmission on the network, we mainly use Windows Sockets technology to transmit data using the now popular TCP/IP protocol. In the design of GIS system, MapInfo is used to make electronic maps and MapX secondary development tools are called to complete the operations of electronic maps. In accessing the database, we use the ADO data interface under the Microsoft ODBC standard to access the database.
5 database management design Considering the performance-price ratio of the system, after the demonstration, the MS SQLSERVER2000 database is adopted. The system database includes a GIS database and a system database. According to the user login information, different permissions are set, and multiple levels of identity such as common operator level, commander level, system management personnel level, and system maintenance personnel level are set, and different usage rights can be used for different levels of users.
The GIS database stores geographic information, including map information and its spatial relationship; the system database includes a positioning information table, a vehicle information table, a communication information table, a vehicle status information table, and an abnormal information table.
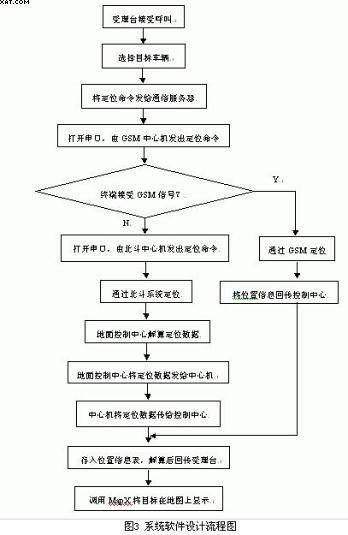
6 Conclusion This system has established a mobile target scheduling system with “Beidou†as the positioning communication means and complete functions. It can effectively locate, track, communicate, command and dispatch real-time mobile targets, and realize the “Beidou†system and GPS. The fusion expands the scheduling scope of the mobile target dispatching system; fully applies the positioning communication function of the Beidou satellite system, integrates the dispatching navigation and communication of the mobile target dispatching system, improves the overall integration of the system, and facilitates the dispatching center to the moving target. Scheduling management.
The positioning part of today's mobile target scheduling system is based on the US GPS or Russia's GLONASS. The mobile target scheduling system based on the Beidou satellite navigation system developed by China is basically not available. By fully drawing on past experience, the vehicle dispatching system established in this paper takes into account the particularity of the "Beidou" system and the functions required for the scheduling of moving target vehicles. The system has been successfully applied to the 120 emergency system, which has won the support and recognition of users and laid the foundation for the application of the Beidou system in other fields.
Z18 Bone Conduction Headphones
Z18 Bone Conduction Headphones,Bone Conduction Headphones Gaming,Wireless Sports Headset,Outdoor Sports Bone Conducting Headset
Shenzhen Lonfine Innovation Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.lonfinesmart.com