Based on a solid state drive (SSD) using flash memory, compared with a traditional hard disk (HDD) based on magnetic disk storage, the solid state drive has: (1) no noise (2) shockproof Dynamic (3) data read and write speed (4) low power consumption and so on. As various flash memory manufacturers continue to introduce more cheaper and higher-capacity flash memory, it will be a trend to replace traditional hard drives with SSDs in the future.
However, since flash memory does not have the repetitive overwrite effect of magnetic disks, a so-called FTL (Flash Translation Layer) program needs to be executed in the SSD device to maintain free blocks that can be idle at any time. Store newly written data. When an idle block is used to store the write data of the client, it is necessary to check whether the number of idle blocks is sufficient. If it is not enough, then the so-called Garbage Collection (GC) is needed to make the number of idle blocks enough to cope with the new data written from the client in the future.
We know that the earlier computer file system (File System) for the deleted files is only on the File Allocation Table, the cluster used by the deleted files is marked as "unused". State, the data stored on the corresponding logical block address (LBA) of these clusters has not been removed. This way of operation is reasonable and appropriate for a traditional hard disk that can be overwritten repeatedly. However, it is not appropriate for non-repeatable SSDs and will require garbage collection. Therefore, in the new ATAPI (ATA Packet Interface) command specification standard, or the NVMe (NVM express) specification standard, the Dataset Management command has been added to allow the more advanced computer file system to be issued to the SSD. "Discard data from certain logical block addresses" to reduce the processing of SSD garbage collection. Not only that, the data set management commands also reduce the Write Amplification Index of the SSD, which extends the life of the SSD.
However, dataset management commands bring benefits to SSDs, but they also present serious problems that are not easily noticeable - the logical physics block mapping table is incorrect! Let us describe the problem of incorrect logical physical block mapping table, how it occurs and the symptoms when the problem occurs.
To simplify the description of the problem, we assume
1 A physical block block has 4 pages
2 Logical block address (LBA) and physical block address (PBA) mapping table, the content is a number pair, respectively representing the block number (block number) and page number (page number), the number of pairs (0,0) Represents no data
3 SSD has 16 logical block addresses
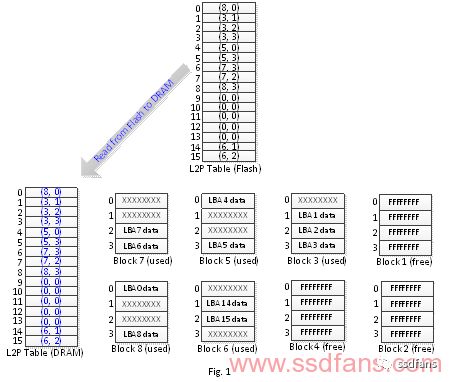
Because the flash memory does not have the characteristics of "repetitive overwrite", the data of a logical block address is not fixed in the flash memory. Therefore, there is a logical physical mapping table (L2P Table) in the solid state hard disk. The function of this map is to let the FTL program find out where the data of a logical block address is stored in the flash memory (including the flash block number, page number, offset (offset). )Wait). This image table needs to be stored in the flash memory, so that the SSD can be powered again after the power is off, to know where the latest data is. For SSDs with high read/write speed, enough Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM) will be configured to store this image table, so that FTL programs can query or update the mapping table more quickly. Therefore, when the SSD starts to supply power, it will read the logical physical mapping table stored in the flash memory to the DRAM, as shown in Fig. 1. (In the figure, the page is marked as FFFFFFFF to indicate that the page is in the erased state; the page is marked as XXXXXXXX to represent that the page has been written to the data but has been replaced by other entity address data or discarded by the data set management instruction to become invalid data)
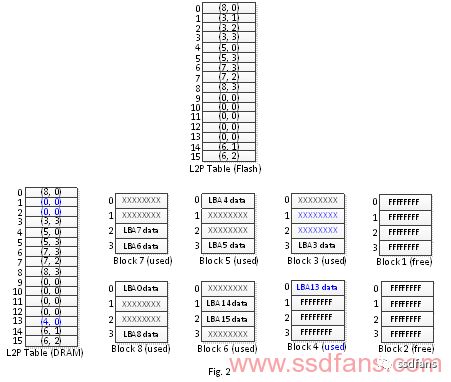
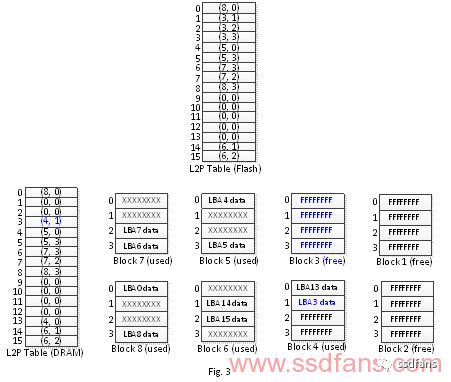
Next, the client deletes the file, issues a data set management command to the SSD, instructs to delete the data of LBA1~2, and then writes the instruction of LBA13. In general, the SSD will perform the following steps (Fig. 2, Fig. 3 illustration):
1. Update LBA1, 2 in the mapping table (DRAM) to (0,0)
2. Require an idle physical block block. Suppose that physical block 4 is taken, the data of LBA13 is written into physical block area 4, and the logical physical block image table of LBA 13 is updated.
3. Find that the number of unused physical block blocks is insufficient (less than 3), start garbage collection, write valid data (LBA3 data) on physical block 3 to physical block 4, and update the logical physical block image table of LBA3. And reclaims physical block 3 as a Free Block.
If the computer system suddenly loses power after the garbage collection is performed after the solid state drive performs garbage collection, the SSD will perform the following steps in the next power recovery (Fig. 4, Fig. 5 Schematic description):
1. Read the logical physical block mapping table stored in the flash memory to DRAM.
2. Read the contents of each page of block 4, and change the logical physical block mapping table on the DRAM according to the corresponding logical block address recorded in the page content.
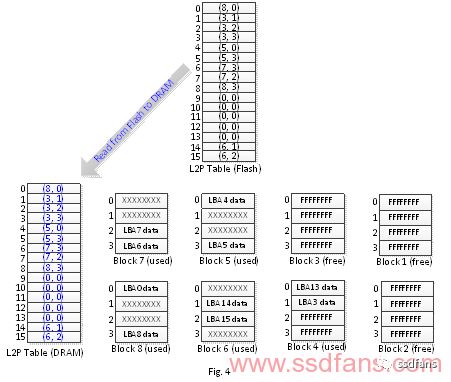
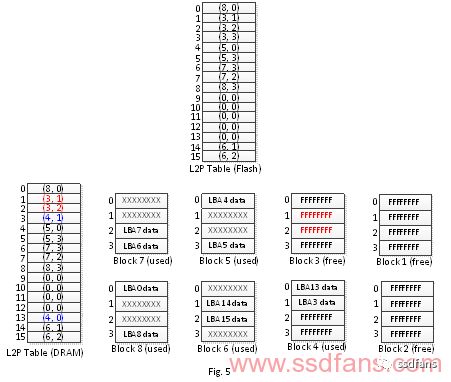
Comparing the contents of Fig. 5 and Fig. 3 mapping table (DRAM), it is found that the physical block corresponding addresses on logical block addresses 1, 2 have different addresses. That is to say, the correctness of the logical physics block mapping table is wrong (Fig. 5 is marked in red)!
The logical physical block mapping table of Fig. 5 shows that the logical block address 1, 2 data exists in the physical block block 3. In fact, physical block 3 is already an idle block and there is no data. Such an error image is a serious mistake for FTL programs. Afterwards, if the SSD continues to be used, after the other logical block data is written into the physical block 3, the read logical block addresses 1, 2 will read the data of the other logical block addresses. As time passes, different data will be written to the physical block 3 at different times, and the data of the read logical block addresses 1, 2 will also change with time. Perhaps the reader will ask, since the data of the logical block addresses 1, 2 has been deleted by the client to release the data set management instructions, it is not important to read what data. However, the reader should be aware that a storage device must have the characteristics of data integrity. If the read data changes over time, the device cannot be said to have the integrity of the data. The reader may also continue to ask, since the data of the logical block addresses 1, 2 has been deleted by the client to release the data set management instructions, the client will not read the data of these addresses. Be aware that the client system is too numerous to enumerate, and the client's program will not read the data at these addresses any more. For example, the storage device is used to form a Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID). One of the hard disks has the problem we described, and the data deleted by the data set management instruction will be read.
The consistency of logical physical block mapping tables and data has always been a problem in SSD design. The market is full of hundreds of solid-state hard drive products, and the quality of designers who have never thought about this problem is worrying. The average SSD buyers often consider the speed of access as a factor of purchase. But smart readers should take the time to understand the designer of the product when purchasing a solid-state hard drive. Is it like Daxin Electronics, which has the leading technical quality of solid-state drives?
In places where the grid availability is zero or where there are high instances of power cut, Off-grid systems are an apt solution for relief from power cuts and they can be installed with a standalone inverter with a separate or integrated charge controller.
If the off-grid system is designed with appropriate solar panels and Battery, it can supply power throughout the year without ever relying on the grid power. If the system is under designed then the battery is always in very low status. We use inverters from reputed brands like Growatt,Goodwe and HuaWei for our off-grid systems.
Off Grid System,Off Grid Solar System,Off Grid Power Systems,Off Grid Solar Power Systems
Wuxi Sunket New Energy Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.sunketsolar.com